- CBD
-
by gu
Therapeutic cannabinoids come from both hemp and marijuana varieties of the cannabis plant. These compounds bind with specialized receptors in the body to elicit a physiological change. But cannabis is not the only source of cannabinoids – in fact, our own bodies produce cannabinoids! They are endocannabinoids and they are vital to our well-being.
Endocannabinoids help regulate our basic needs and instincts. For example, the endocannabinoid, anandamide (AEA), controls memory, minimizes pain, and regulates eating and sleeping patterns. Some studies suggest AEA might play a role in fertility, as well. Another endocannabinoid found primarily in the brain, 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), may be involved in roughly 85 percent of brain activity.
However, sometimes, the body cannot adequately produce and absorb endocannabinoids. Though research is limited, one study suggests a possible link between conditions like fibromyalgia, migraines, and gastrointestinal illnesses and inadequate endocannabinoid levels. Fortunately, Mother Earth has gifted us with an easy solution: phytocannabinoids.
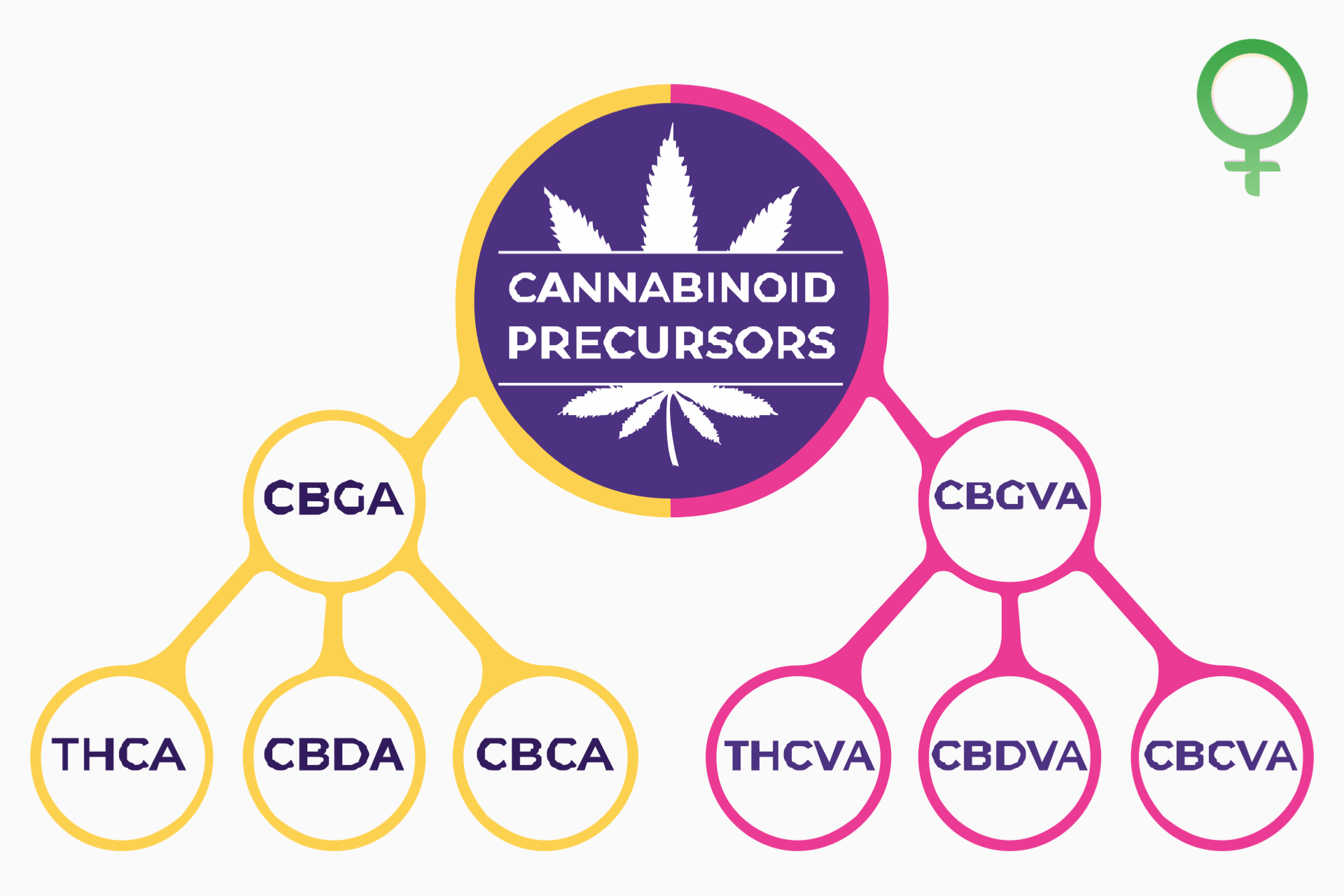
Therapeutic Cannabinoids Found in Hemp
The cannabis plant (which includes both hemp and marijuana), contains more than 100 phytocannabinoids (a.k.a. plant-based cannabinoids), most of which have yet to be studied. Those that we have reviewed, though, show some pretty promising things!
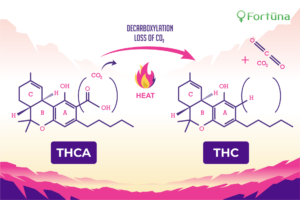
Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
Topping our list of cannabinoids is Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol or THC, the psychoactive chemical responsible for cannabis’s drug-like effects. THC is also significant because it, alone, is what distinguishes hemp – a federally-legal substance – from its much more controversial cousin, “marijuana.” THC may cause feelings of euphoria, introspection, confusion, memory loss, or altered sensations – a state commonly referred to as “high.” Potential therapeutic benefits of THC include pain relief, appetite stimulant, and suppression of muscle spasms.
Cannabidiol (CBD)
It took some time, but CBD is finally getting the recognition it deserves. The non-psychoactive cannabinoid is flooding headlines with news of its therapeutic potential. According to research, a few of CBD’s potential therapeutic applications include pain relief, anti-seizure, reduced inflammation, blood sugar control, anti-bacterial and -fungal, and improved bone density. Despite years of limitations, CBD cultivation, processing, and sale are now federally legal and CBD research easier to conduct. The new legislation will not only result in better access to CBD research but will also improve consumer protections.
Cannabidivarin (CBDV)
Cannabidivarin is similar to cannabidiol in both structure and effect. Like CBD, CBDV is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid widely hailed for its ability to treat seizures. CBDN also shows promise for its anti-nausea and anti-inflammatory properties. Strains with a high CBD potency also tend to have a high CBDV content, as well.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
THCV is a psychoactive cannabinoid but only in extremely high doses. This special cannabinoid undergoes a unique metabolic process compared to other cannabinoids whereby divarinolic acid joins with geranyl phosphate to create THCv acid. When THCv acid is heated (decarboxylated) and ingested, it can suppress appetite, reduce seizures, lower blood sugar, and improve bone density. Though high doses can cause mild psychoactive effects, the experience is usually short-lived. As such, THCv is not a federally-scheduled substance.
Cannabichromene (CBC)
Cannabichromene is a minor cannabinoid with no psychoactive properties. Like other therapeutic cannabinoids, studies suggest CBC may be beneficial in relieving pain, assisting digestion, and reducing inflammation. CBC is also an anti-bacterial and anti-fungal and may help treat neurodegenerative diseases by regenerating brain cells. But perhaps the most exciting thing about CBC is the way it regulates the effects of other cannabinoids including both phyto (plant) cannabinoids and endo (internal) cannabinoids.
Cannabichromevarin (CBCV)
Cannabichromevarin is very similar to CBC in structure and possesses many of the same therapeutic benefits, as well. Unfortunately, research on CBCV is limited which makes it difficult to determine its therapeutic properties. Some suggest that CBCV could benefit conditions such as chronic pain, arthritis, depression, Chron’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, insomnia, osteoporosis, and more.
Cannabigerivarin (CBGV)
CBGV is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that improves the absorption of cannabinoids like THC, CBD, and more. Some of the therapeutic value of CBGV includes analgesic (pain-relieving), and anti-inflammatory properties. It may also combat skin conditions like psoriasis and excessively dry skin. Additionally, CBDV and other therapeutic cannabinoids hold promise for the treatment of some cancers. According to a 2013 study from the University of St George’s London,
“These agents[ CBD, CBG, and CBGV] are able to interfere with the development of cancerous cells, stopping them in their tracks and preventing them from growing. In some cases, by using specific dosage patterns, they can destroy cancer cells on their own.”
Therapeutic Cannabinoids in Hemp Versus Marijuana
The difference between the psychoactive plant, marijuana, and its non-psychoactive cousin, hemp, lies only in its THC content. If the plant contains more than .3 percent THC, it’s marijuana; if not, it’s hemp. The distinction first came about in 1946 with the passing of the Agricultural Marketing Act, which clearly defined hemp as any part of the cannabis plant with less than .3 percent THC. Though THC is limited in hemp plants, other cannabinoids are not. As such, hemp is a valuable source for a full spectrum of non-psychoactive cannabinoids
Despite its clear distinction, hemp and marijuana have long endured the same political red tape. Recent legislation, however, makes it easier to produce, extract, and sell therapeutic cannabinoids from the hemp plant without the same federal restrictions marijuana faces.
Understanding Labels; Hemp Products do not Always Contain Therapeutic Cannabinoids
Hemp — especially hemp flower — is an excellent source of therapeutic cannabinoids. However, when it comes to product labels, hemp does not always equal cannabinoids.
To be clear, hemp seeds, leaves, and stems are indeed a great source of nutrition and other health benefits. For example, hemp oil (made by pressing hemp seeds) contains an abundance of vitamins and fatty acids which can improve skin conditions. Likewise, hemp leaves are among the most nutrient-dense vegetables available, second only to soy. So, yes, general hemp products do have therapeutic benefits, but not necessarily therapeutic cannabinoids.
Those interested in trying hemp cannabinoids should pay close attention to product labels and brand credibility. It’s easy to get lost among a sea of buzz words like “CBD” and “hemp therapy,” and difficult to distinguish between legitimate businesses and snake oil salesmen.
It is up to the consumer to decide which businesses are best and which are best to forget. However, there are a few tips anyone can use to determine which hemp companies offer the best CBD products on the market.
- Check Labels: Anyone using cannabinoids as a marketing tactic will clearly label them on product packaging. Products that only list “hemp oil” likely do not contain significant cannabinoid concentrations.
- Check Reviews: Happy customers often share their experiences online; disappointed customers almost always do. If a product is (or isn’t) worth the purchase, someone online will talk about it. Pull reviews from multiple sources (not just the company website) to get the best clearest idea of product quality.
- Confirm Company Contact Info: Legitimate businesses will run legitimate business operations which includes clear and easy access to the company’s contact information. Contact information should include both an email address and phone number at minimum, though an actual street address is ideal.
Concluding Our thoughts on Therapeutic Cannabinoids
No matter their source, cannabinoids hold incredible therapeutic potential. Whether created internally or supplemented from an outside source, cannabinoids can improve health and well-being in some fantastic ways.
Contact us to learn more about the therapeutic cannabinoids found in hemp, or to get started on your next feminized hemp seeds crop. We look forward to speaking with you.



